Health officials in Pueblo County, Colorado identified a bubonic plague case. The infected person was hospitalized but their condition improved.
Plague is endemic to the area, making it difficult to pinpoint the source. Colorado has reported 66 human plague cases since 1957.
Plague Transmission and Prevalence
Yersinia pestis bacteria cause bubonic plague. Infected fleas, often carried by rodents, transmit the disease to humans.
The U.S. averages seven human plague cases annually. Southwestern and Western states report most cases, with 496 cases nationwide from 1970 to 2020.
Symptoms of Bubonic Plague
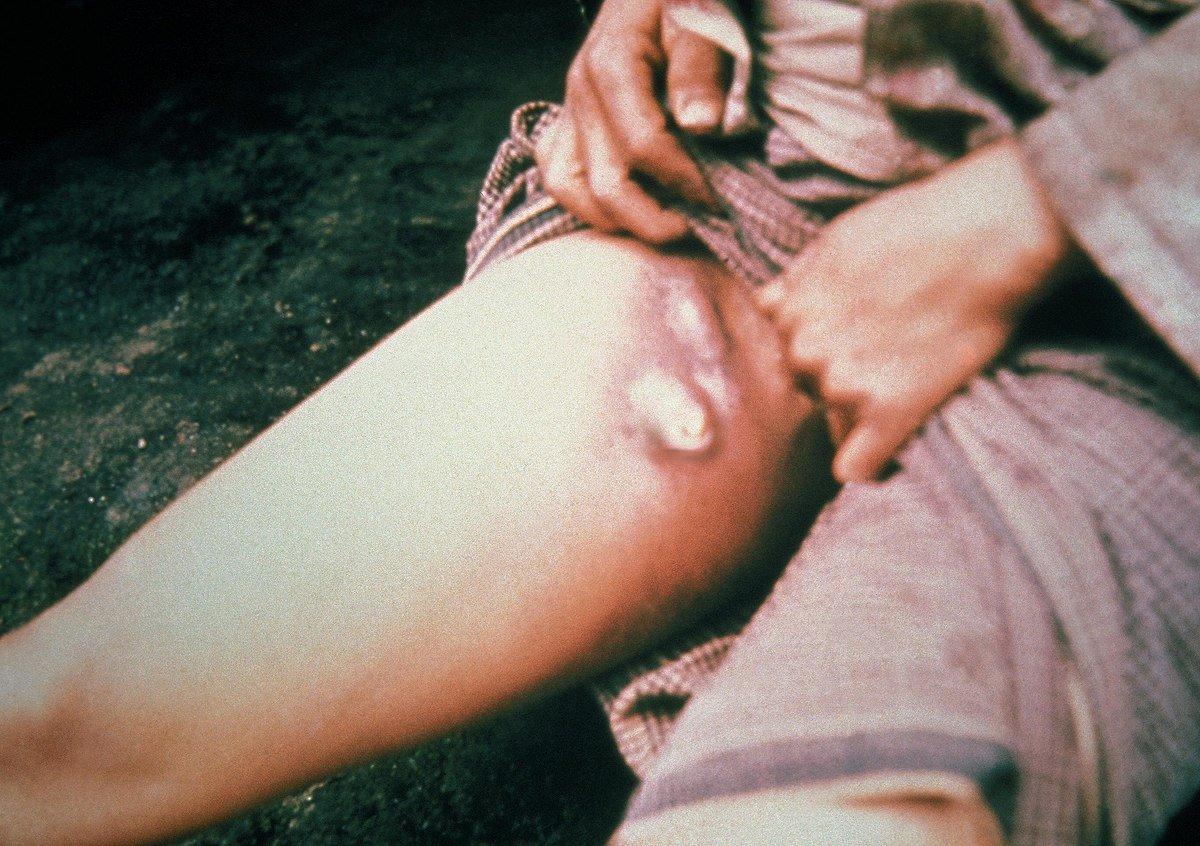
Plague symptoms develop within 1-7 days after exposure. Patients experience sudden fever, chills, headaches, and muscle aches.
Swollen lymph nodes (buboes) characterize bubonic plague. Buboes can grow from less than 0.5 inches to 4 inches in size.
Other Plague Forms Exist
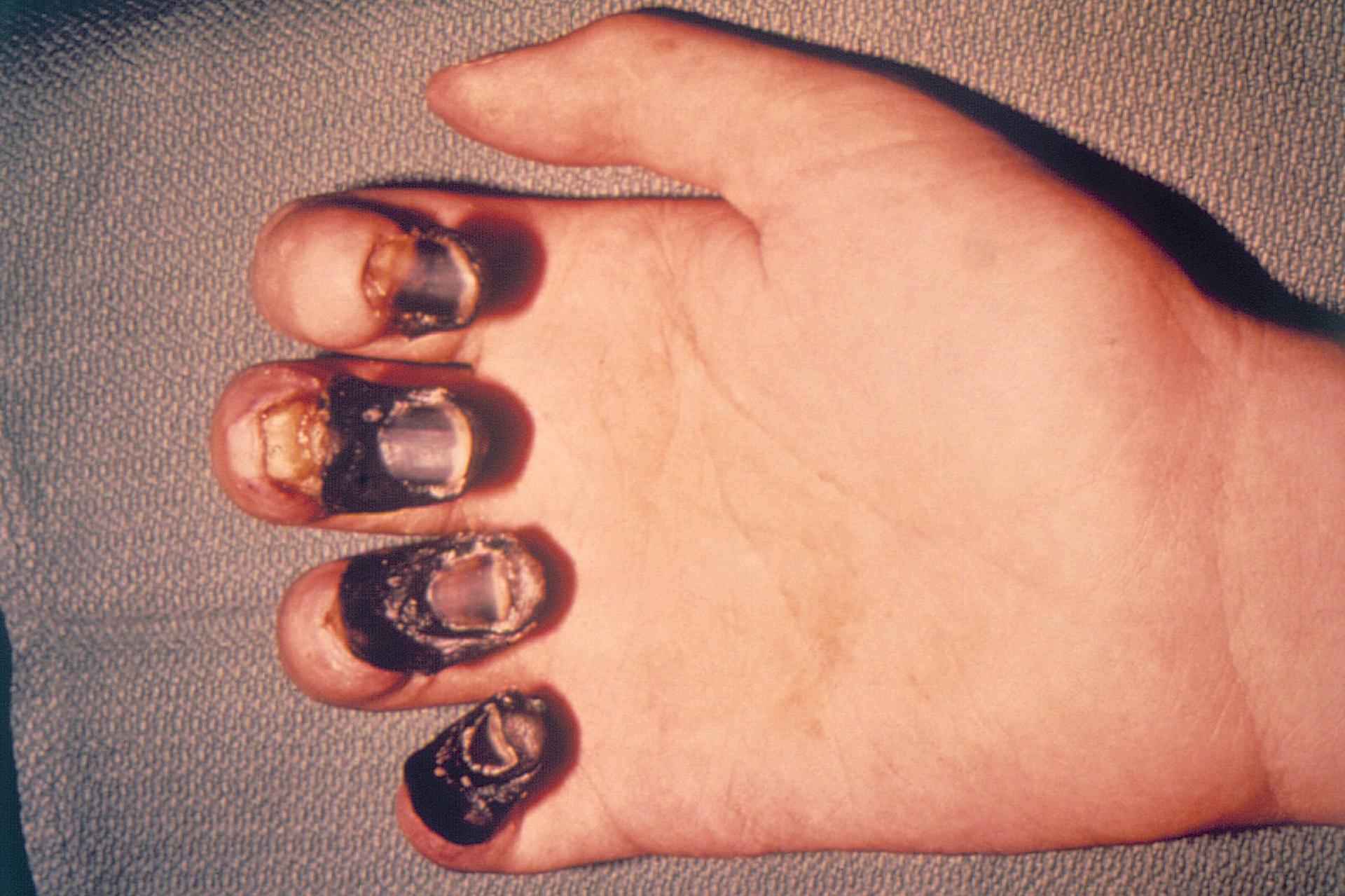
Pneumonic plague infects the lungs and can spread person-to-person. Septicemic plague occurs when bacteria infect the blood.
Pneumonic plague has a 100% fatality rate if untreated. The WHO estimates 30-60% of untreated bubonic plague cases are fatal.
No U.S. Plague Vaccine
The United States lacks a plague vaccine. Immediate medical attention is crucial for survival.
Antibiotics effectively treat plague if administered promptly. Delayed treatment significantly increases the risk of death.
Preventing Plague in Humans
Officials advise clearing areas where rodents breed. Pet owners should prevent pets from roaming in rodent-infested areas.
Regular flea treatment for pets is recommended. Flea collars are not proven effective against plague-infected fleas.
Handling Dead Animals Safely
People should avoid contact with dead animals. Use insect repellent with 20-30% DEET when handling carcasses.
Long-handled shovels help maintain distance from potentially infected animals. Proper disposal in outdoor garbage bags is essential.
Plague’s Global Impact History

Plague has affected all continents except Oceania. The 14th century Black Death killed an estimated 50 million people.
It wiped out over 25% of Europe’s population. Some estimates place European deaths as high as 60%.
Endemic Countries and Outbreaks
The Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, and Peru report most plague cases. China and India experienced significant outbreaks after the Black Death.
Madagascar reported 2,417 cases and 209 deaths from 2010 to 2015. Peru averages 6.5 cases per year since 2010.
U.S. Plague History Examined
Plague entered the U.S. via rat-infested ships around 1900. San Francisco experienced early outbreaks, leading to misguided racist policies.
Los Angeles suffered the largest U.S. urban epidemic in the 1920s. These outbreaks established plague reservoirs in Western rodent populations.


