Dengue fever cases reach record 10 million globally. This represents approximately 1 in 800 people on Earth.
The virus spreads to previously unaffected countries. Historically, dengue infections have quadrupled globally between 2000 and 2015.
CDC Issues Warning for Travelers

The Centers for Disease Control alerts about increased dengue risk. They urge travelers and healthcare providers to stay vigilant.
This warning follows a 30-year trend of rising dengue cases. The CDC reported a 300% increase in dengue cases from 2000 to 2019.
Climate Change Fuels Mosquito Spread
Rising temperatures expand mosquito habitats northward. Heat benefits both mosquitoes and the dengue virus.
Aedes aegypti mosquitoes now survive in 50% more US land area than in the 1980s. Scientists project a potential 50% increase in dengue-suitable areas by 2080.
Aedes Aegypti: The Tenacious Vector

Aedes aegypti mosquitoes adapt well to urban environments. They breed in small water containers around homes.
These mosquitoes can fly up to 400 meters in their lifetime. One female Aedes aegypti can lay up to 200 eggs in a single batch.
Dengue’s Impact on Global Health
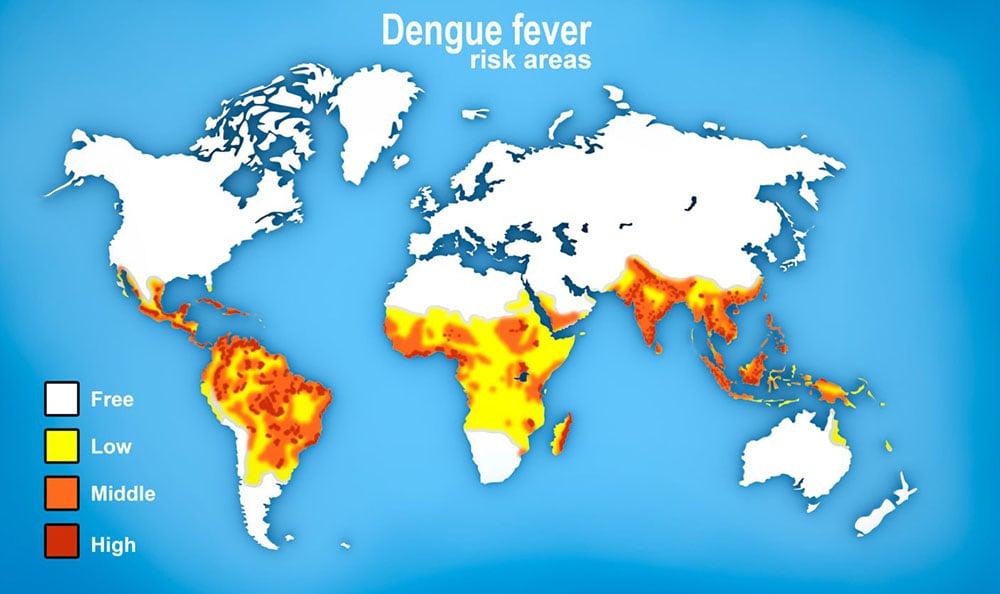
Dengue infects 390 million people annually. It causes about 20,000 deaths each year.
The economic cost of dengue exceeds $8.9 billion annually. WHO reports a 30-fold increase in global dengue cases over the past 50 years.
Puerto Rico: A Dengue Hotspot

Puerto Rico experiences significant dengue outbreaks. The island reported over 50,000 cases in its worst epidemic in 2010.
Dengue costs Puerto Rico an estimated $38 million annually. The territory serves as a potential gateway for dengue into mainland US.
Vaccine Development Faces Challenges
France discontinued its dengue vaccine due to low uptake. Dengue’s four serotypes complicate vaccine development.
Only one dengue vaccine is currently WHO-approved. Vaccine development typically takes 10-15 years and costs up to $1 billion.
Projected Increase in Dengue Exposure
Scientists predict 2 billion more people at risk. This projection assumes continued global temperature rise.
Currently, about half the world’s population lives in dengue-risk areas. Annual dengue infections could reach 60 million by 2080.Currently, about half the world’s population lives in dengue-risk areas. Annual dengue infections could reach 60 million by 2080.
Mosquito Control Efforts Intensify

Communities implement larvicide and water management strategies. Some areas experiment with genetically modified mosquitoes.
The US spent over $1 billion on mosquito control in 2022. Effective mosquito control can reduce dengue cases by up to 70%.
Individual Prevention Measures Crucial

Travelers should take precautions in dengue-risk areas. Using insect repellent and covering exposed skin helps prevent bites.
Eliminating standing water around homes reduces breeding sites. Personal protection measures can reduce bite risk by up to 90%.


